An AC-DC power supply or adapter is an electrical device that obtains electricity from a grid-based power supply and converts it into a different current, frequency, and voltage. AC-DC power supplies are necessary to provide the right power that an electrical component needs.
AC-DC power supply deliver electricity to devices that would typically run on batteries or have no other power source. Here’s what you need to know about AC-DC power supplies and the solutions that FSP Group can offer for your power conversion needs.
What is an AC-DC power supply?
In a nutshell, an AC-DC power supply converts one type of electricity (AC - “alternating current” into DC - “direct current.” Each day, most people will undoubtedly use electrical devices that require both types of electricity.
For example, your car requires a 12v DC electricity supply to operate. And mains power gets supplied to homes and businesses from an AC electricity supply. Sometimes you’ll need to convert AC to DC, and that’s why you’ll need an AC-DC power supply.
What is AC power?
AC or Alternating Current is the standard type of electricity supplied from the electrical grid to homes and businesses. It’s called AC because of the waveform that the electrons take. Sometimes, the current reverses and changes its magnitude.
AC power’s voltage and frequencies differ between regions; for example, the United States uses 120 volts at a frequency of 60 Hz. Across the Atlantic, the United Kingdom uses 230 volts at a frequency of 50 Hz.
Because AC power moves in waves, it can travel a lot further than DC power, hence why it gets used in electrical grid systems across the world. While many electrical devices use main-supplied AC power, others need converting to DC electricity.
AC power first became widespread in the late 19th century thanks to early electrical pioneers’ efforts, such as Nikola Tesla and Sebastian de Ferranti.
What is DC power?
DC or Direct Current is the other type of electricity used in various applications. Unlike AC, the path that electrons take in DC power is linear. You’ll find electrical devices like batteries, solar and fuel cells, and alternators use DC electricity instead of AC.
An advantage DC power has over AC is its consistent delivery of voltage to electrical devices. However, a disadvantage of DC power is that it can only run across short distances, making it unsuitable for the electrical grid.
Most electronic items require DC electricity due to the ‘clean’ delivery of power. Of course, mains electricity gets provided as AC power, so an AC-DC power supply converts the electricity to DC power.
All AC-DC power supplies have rectifiers built into them and transformers to raise or lower voltage levels where necessary. Rectifiers are the components in power supplies that convert AC power to DC.
DC electricity dates back to the late 19th century and is most commonly associated with early electrical pioneers like Thomas Edison.
Why are there two different power types?
As you can imagine, electricity was a hot topic in the late 19th century. Both Nikola Tesla Edison and Thomas Edison were virtually competing against each other to create the “best” type of electrical current.
Both AC and DC electricity have their advantages and limitations, and that’s why they get used equally in various electric applications. AC power is an excellent way to deliver electricity over long distances and is suitable for distribution via a mains grid system.
DC power provides a more linear and reliable form of electricity, but at the cost of distance. It’s clear that AC power dominates the electrical world, but DC power is a must when powering electronic items at home or in the workplace.
AC Power vs DC Power Comarison
| Type | AC Power | DC Power | AC-DC Power Supply |
| Definition | The standard type of electricity supplied from the electrical grid to homes and businesses. | The other type of electricity used in various applications. | Take AC electricity from a source and convert that energy into DC electricity. |
| Electric current | Waveform | Linear | From waveform to linear |
| Advantage | An excellent way to deliver electricity over long distances and is suitable for distribution via a mains grid system. | Provides a more linear and reliable form of electricity, but at the cost of distance. | Increase or decrease voltage levels when necessary to provide a reliable source of DC electricity to a device. |
| Applications | Powering electronic items at home or in the workplace. | Batteries, solar and fuel cells, and alternators. | External adapters that plug into laptop computers, and internal converters like in all electronics from DVD players to medical equipment. |
How does an AC-DC power supply work?
An AC-DC power supply is a necessity for today’s electronic devices. You’ll find them in various formats, such as external adapters that plug into laptop computers, and internal converters like in all electronics from DVD players to medical equipment.
Each AC-DC power supply will have different design configurations, but the basic principles remain the same. For instance, an AC-DC power supply will have one or more transformers, rectifiers, and filters.
Transformers are passive electrical devices that transfer electricity from one circuit to another. Their job in an AC-DC power supply is to increase or decrease voltage levels when necessary to provide a reliable source of DC electricity to a device.
Rectifiers take AC electricity from a source (such as mains power) and convert that energy into DC electricity. And the job of filters is to remove electronic ‘noise’ from low and high AC power waves.
What happens if you don’t use an AC-DC power supply?
While it’s true that some household and commercial electrical items only use AC power, many other applications demand DC power. What happens if you try to supply AC power to an electrical device that requires DC electricity?
The short answer is simple: bad things will happen! Electrical devices with electronic components will almost certainly get destroyed, and some high AC voltage equipment may even explode or catch fire.
There’s also the risk to human life if you apply AC power to an electrical device that requires Direct Current. That’s why it’s always essential to use an AC-DC power supply when the electrical requirements demand it.
Types of AC-DC Power Supplies
There are many different options on the market for selecting an AC-DC power supply for your requirements. Innovations in electrical technology have made it possible to have AC-DC power supplies that are compact yet fully meet even the most demanding of application needs. Keeping that in mind, how can you choose the right one?
There are three types of AC-DC power supply that you can consider; the one you need will ultimately depend on your application and power conversion needs:
AC-DC Power Supply Adapters
Virtually everyone will have seen an adapter-style AC-DC power supply - commonly known as an “AC Adapter.” They get used for various applications such as laptop computers, computer monitors, televisions, and other household and commercial electronics.
Adapters are external power supplies typically enclosed in a compact, sealed unit for safety and aesthetic reasons. You may need an adapter-style AC-DC power supply if you wish to convert AC power to DC for portable devices or household and commercial electronics.
FSP Group designs and manufactures AC adapters that output power between 10W and 330W and 5V to 54V. Much of our range of adapter-style AC-DC power supplies meet DoE Level VI compliance.
Our range of AC adapters is ideal for applications such as mini-ITX PCs, laptops, POS and PoE systems, embedded systems, monitors and televisions, printers, and communications systems.
View our range of AC-DC power supply adapters。
Open Frame Power Supplies
An open frame power supply is when the AC-DC power supply components get installed on a circuit board with no protective cage or enclosure. The enclosure of the electrical equipment typically provides the physical protection necessary.
Open frame power supplies are the default option for AC-DC conversion requirements. They’re extremely popular for several reasons:
Customization - pen frame power supplies can easily get situated in a convenient and safe location within the chassis of any electrical devices;
Different form factors - FSP Group manufacture open frame power supplies in two-inch by four-inch form factors and three-inch by five-inch. We can also build open frame power supplies according to your unique designs and specifications;
Wattage and voltage options - FSP’s open frame power supplies range from 30W to 450W and 5V to 54V output voltage (including 12V+54V).
View our range of open frame power supplies.。
Industrial PC Power Supplies
Both adapters and open frame power supplies are suitable for low-power applications, but what happens when you have an industrial PC with more demanding electrical requirements for AC-DC conversion?
To meet those needs, you should narrow your search down to industrial PC power supplies. They are AC-DC power supply products specifically for PCs used in industrial settings that boast comprehensive wattage options.
Each industrial PC power supply unit gets designed with high reliability and power density in mind, and the solutions offered by FSP Group meet IEC 62368 and IEC 60950 safety standards.
Aside from needing an AC-DC power supply with higher wattages in mind, you’d also consider one for the following reasons:
Extreme operating environments - industrial power supplies can cope with extreme temperatures and have a high MTBF (mean-time before failure) rating;
High energy efficiency - many of FSP Group’s industrial power supplies have 80 Plus Gold and Platinum certification.
Our range of industrial PC power supplies are available for the following form factors:
Flex;
1U and 2U;
ATX and SFX;
1U and 2U redundant;
CPRS module and 2U CPRS;
PS2-redundant and Mini-redundant.
They’re available from wattages as low as 100 W and as high as 3,000 W. Our industrial PC power supply units are also available with input voltages including 115 V AC, 230 V AC, LVDC and HVDC.
View our range of industrial PC power supplies.。
Other types of AC-DC power supplies
While the above three options are the most common ones in daily use, there are, of course, other types of AC-DC power supplies available. They include ones used in PC cases, available in a range of form factors, medical power supplies, and TV power supplies. Other solutions, also available from FSP Group, include AC-DC power supplies for solid-state lighting and PV (photovoltaic) inverters for use with solar cells.
Other solutions, also available from FSP Group, include AC-DC power supplies for solid-state lighting and PV (photovoltaic) inverters for use with solar cells.
With the rapid developments in the eSports industry in recent years, general office desktop PCs are becoming inadequate in sustaining the hardware requirements for gaming. Gamers have a certain level of demands in visual effects; with high-end video cards installed, and demanding faster processing speed in the CPUs, the standard for other hardware is also on the rise. In order to provide a relatively stable power output at a low energy consumption rate, a low-quality power supply will not be able to meet the demands of the professional gamers. The FSP Group is a professional power supply brand. Today we share a few keys for our audiences in how to choose a power supply:
80 Plus efficiency certification
80 Plus is a third-party standards of fairness specifically for power supply conversion efficiency. It currently has groups of White, Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, and Titanium in energy efficiency standards. With the exception of most energy-efficient Titanium standard, which requires the power supply to meet a demanded ratio while under a 10% load, other groups require a certain energy efficiency level to be reached while under a 20%, 50%, or 100% load.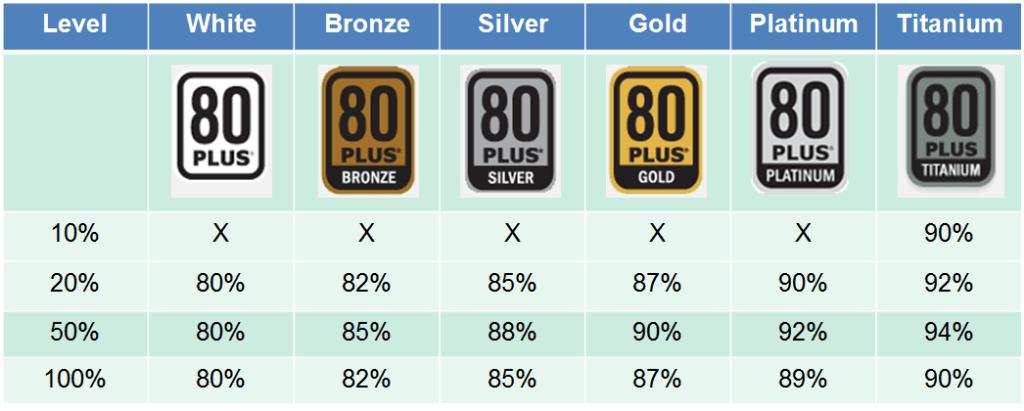
Safety Standard Certification
In many countries, safety standard certifications are required for electrical appliances in order to ensure the safety of their citizens. Only certified merchandise can be sold in the market with the aim to prevent bodily harm from electric shocks, energy hazards, fires, mechanical hazards, heat hazards, radiation hazards, and chemical hazards, to ensure a certain safety standard in the products. Universal safety specifications include CE/CB/UL/TUV/FCC/CCC, etc., and FSP products have all applied for the local safety specifications in accordance with the demands of the clients or sales region.Maximum Power Output of Each GroupConforming to the demands in safety specifications, power supplies should come with rating labels, indicating the AC input range of the product applying for the safety specifications, as well as the maximum DC output or combined output of each group. For general desktop PC gamers, attention should be paid to the maximum combined output power under the group +12V. In general, a single output unit that is able to match the full rated output of the power supply is considered good. The list below is the rating label of a FSP Aurum PT 1200W, with a full output of 1200W. This model is designed to be a single 12V output unit with a maximum output of 1200W.
Appearance DesignOther than considering the performance of the products in choosing PC hardware, many gamers would also pay attention to the style of the components in their PCs. Designers have long been committed in designing hardware with aesthetic values, power supplies have too, with the hard work of many brand manufacturers, broke through the stereotype of being simply a cube, and developed their own aesthetics in design. Under this trend, the FSP Group also came up with its own exclusive asymmetrical Hydro G series power supply. The internal components are designed with thermal design concepts, and the best cooling vent design is drawn up from heat laboratory assessments, combined with a stylized fan guard, creating a both aesthetically pleasing and efficient product, as seen below.

Output Voltage RegulationPower output quality affects the stability of the computer system. Too high a voltage may cause hardware damage, while too low a voltage may cause the computer to freeze or reboot. Therefore, the output voltage regulation of a power supply is regulated and demanded. In the field of power electronics, voltage regulation also categorized regulations caused by input voltage regulations as line regulations, and regulations due to load variants as load regulations. The commonly used term “voltage regulation” in the power supply industry, is the sum of the two regulations combined. Below is the power supply voltage regulation standards formulated by Intel.
Outputs +5V +12V -12V +3.3V +5Vsb Vout Range(V) Min 4.75 11.40 -10.80 3.135 4.75 Max 5.25 12.60 -13.20 3.465 5.25 Regulation Limit ±5% ±5% ±10% ±5% ±5% With the rapid developments in the eSports industry in recent years, the demands in computer hardware is getting higher and higher. The voltage stability formulated by Intel should serve as a guarantee on computer system operations, but it does not satisfy the gamers, who demands a ±3% or ±1% on primary output such as +12V, +5V, and +3.3V.
Ripples and Noises
Ripple: The synchronized composition of a type of input frequency and switching frequency overlapping on top of AC outputs. Noise: High-frequency noises outside of ripples. The sum of these two is one of the important Intel regulations in power supplies. This is to mainly prevent the heating of
electrolytic capacitors on top of the receiving hardware caused by too much ripples and noises. When heated up, the capacity of the electrolytic capacitors will change, and impact hardware performance, as well as leakage in the electrolytic capacitors in severe scenarios, short circuiting and burn the PCB, impacting the lifespan of receiving hardware such as the motherboard, video card, hard disks, and so on. Please refer below for the ripple and noise standard from Intel:Output Rail Maximum Ripple & Noise (mVp-p) +12V 120 +5V 50 +3.3V 50 -12V 120 +5Vsb 50 In recent years, many gamers have learned the importance of this standard, and brand manufacturers are also providing quality products. Taking the current high-end products as an example, their primary outputs, such as +12V, can already suppress the ripples and noises to 20mV or below, also becoming a consideration for gamers in selecting products.

